This project is a simple 2-transistor VHF power amplifier, with about 16dB gain, and requires no tuning or alignment procedures. Wideband techniques have been used in the design and the circuit is equipped with a "lowpass" filter to ensure good output spectral purity. The project has been designed for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board. The circuit is specifically designed to amplify the output of 7mW to 10mW WBFM transmitters (wide band) to a final level of 250mW to 300mW, after the filter.
This project is a simple 2-transistor VHF power amplifier, with about 16dB gain, and requires no tuning or alignment procedures. Wideband techniques have been used in the design and the circuit is equipped with a "lowpass" filter to ensure good output spectral purity. The project has been designed for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board. The circuit is specifically designed to amplify the output of 7mW to 10mW WBFM transmitters (wide band) to a final level of 250mW to 300mW, after the filter.

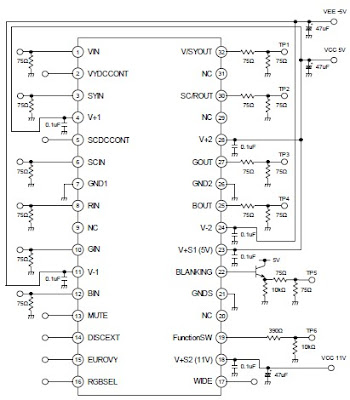
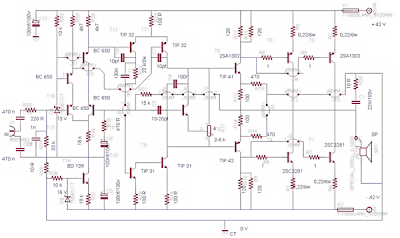
Circuit Description
The first stage (Q1) operates in Class-A. Although Class-A is the least efficient mode, it does offer more RF gain than other clases of bias, and Q1 is a low-level stage, when compared to the higher power Q2 stage. The output of this stage is around 70mW of RF power. The stage is
untuned so that it gives a very broadband characteristic. The transistor is biased by means of R5, R6 and L6, and the residual (standing) DC current is set by R4. The input signal is coupled by C9 to the Base of the transistor. Q2 is operated in Class-AB which leads to greater efficiency, but the RF gain is only about 8dB, but it amplifies the output of Q1 to typically 250mW. Q2 is
biased by means of R3, R2 and L4. The input signal from Q1 is coupled to the Base of Q2 via C7.
The voltage regulator Q3 (78L08) is used to regulate the supply voltage to Q1 and the bias votages to both Q1 and Q2 so that the output RF power is relatively constant, even with large variations of supply voltage. Q3 also removes supply ripple as well as providing power for an
FM transmitter like Kit 3018 wireless microphone with the required DC 8v power.
The output of the amplifier is filtered with a low-pass filter to reduce the output spurious and harmonic content. The output filter consists of C3, C4, L1 and L2.
COMPONENTS
Resistors 5%, 1/4W, carbon:
10R R1 brown black black
22R R7 red red black
47R R3 yellow orange black
120R R4 brown red brown
470R R2 yellow violet brown
2K2 R5 red red red
4K7 R6 yellow violet red
2N2369 Q1
2N4427 Q2 1
Ceramic caps
33p C3
47p C4
1n C5 C6 C7 C8 C9
10n C1 C11
Ecaps:
220u/16V C2
10u/25V C10
78L08 Q3
RFC L4 L5 L6
Ferrite L3
3 turn coil L2
5 turn coil L1
2 pole terminal block
HS106 heatsink (